If you’re new to forex, there’s a term that keeps popping up in every guide, chart, and strategy video—liquidity. I didn’t really get it at first either. It sounded like finance-speak only bank analysts understood. But once I grasped how it worked, it instantly clicked why my trades weren’t always filling right or why spreads were eating into my profits.
I used to trade exotic pairs thinking they were “less crowded” and more “unique”. But what I didn’t know was that lower liquidity in those pairs meant higher costs and slower execution. It was like shopping at a tiny gas station instead of a busy supermarket—fewer options, higher prices, and longer waits.
Now that I’ve been trading for years, I always start my day by checking liquidity levels. If you want tighter spreads, faster fills, and lower risk of weird price spikes, you have to pay attention to liquidity.
In this article, you’ll learn:
- What forex liquidity really means in simple terms
- How to measure liquidity using trading data
- Why it matters for your costs, risk, and strategy
- What makes some currency pairs more liquid than others
- How to use this knowledge to your advantage
Stick with me and by the end, you’ll trade smarter, faster, and with more control over your outcomes.
What Is Liquidity in Forex?
Understanding the Basics
Liquidity in forex is how quickly and easily you can buy or sell a currency pair without changing the price much. When a market is liquid, orders are filled fast at prices close to what you expected. When it’s not, your trade can get delayed or filled at a worse price—this is called slippage.
Here’s how I explain it to friends: trading in a liquid pair like EUR/USD feels like grabbing water from a fountain. You press a button, and it flows instantly. Trading in something like USD/TRY feels more like trying to get sap from a tree—you’ll get some, but it’ll take time and tools.
High vs Low Liquidity
High liquidity means there are tons of buyers and sellers in the market. That keeps spreads tight and prices stable. You see this in pairs like:
- EUR/USD
- USD/JPY
- GBP/USD
On the flip side, low liquidity pairs—often called exotic pairs—like USD/TRY or EUR/ZAR are more volatile. There just aren’t enough people trading them all the time, so prices jump faster and spreads widen a lot.
How It Works in Real Time
Last week, I tried placing a buy order on EUR/USD right after the NY session opened. Boom—filled instantly at the price I clicked. Later, I tested the same on USD/MXN. Not only did the fill take longer, the spread was 6 pips wider. That’s liquidity in action.
How to Measure Forex Liquidity
Use Trading Volume as a Clue
Most forex platforms don’t show centralized volume (since forex is decentralized), but you can use proxies like the number of price ticks or depth of market (DOM) if available. I personally watch how often price updates and how tight the bid-ask spread is. More ticks per second = more liquidity.
Major Pairs vs Exotic Pairs
Here’s a quick comparison that I put together from my own trades and broker data:
| Pair | Liquidity Level | Typical Spread | Volatility Risk |
|---|---|---|---|
| EUR/USD | High | 0.5 – 1.2 pips | Low |
| GBP/JPY | Medium | 2 – 3 pips | Moderate |
| USD/TRY | Low | 6 – 12 pips | High |
As you can see, the more exotic the pair, the more you pay—and the more unpredictable the price action.
Broker Tools and Platforms
I’ve used platforms like MetaTrader 4 and cTrader to get real-time liquidity info. Some brokers offer Level II order books or “market depth” tools, which show you where buyers and sellers are stacked. These help you avoid trading into illiquid zones where prices can spike.
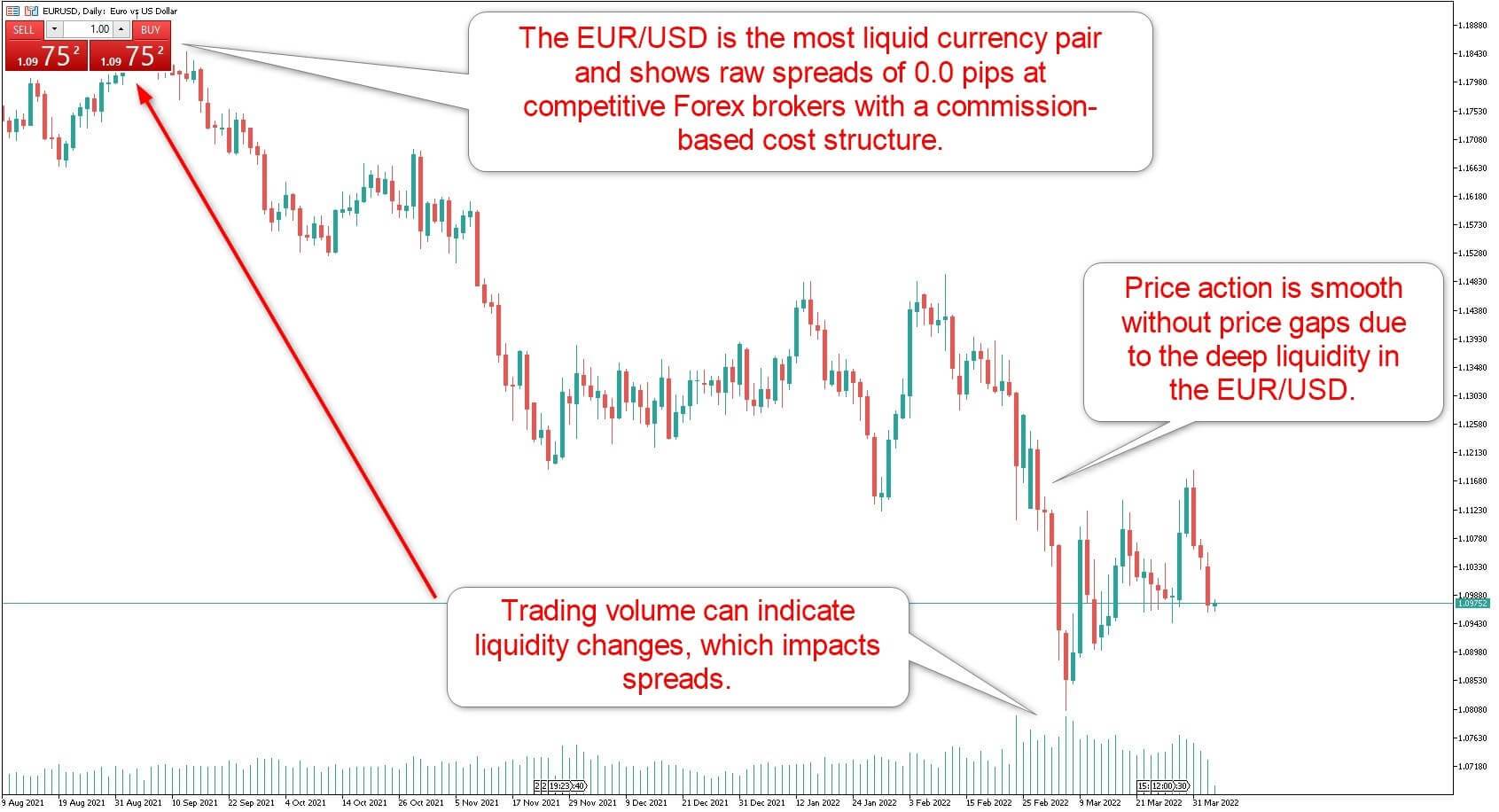
Why Liquidity Matters in Forex Trading
Lower Spreads = Lower Costs
In liquid markets, you get tight spreads—the gap between the buy and sell price. That means less money out of your pocket on every trade. I used to ignore spreads. Big mistake. I ran a backtest comparing trades with 0.8 pip vs 3.5 pip spreads. After 100 trades, I was down $135 just in spread costs.
Faster Execution and Less Slippage
Slippage is when your order fills at a different price than expected. It’s sneaky and eats into your gains. But when there’s enough liquidity, your orders get matched instantly. The last time I got hit with 8 pips of slippage? It was trading AUD/NZD during the Asia session. Never again.
Stable Prices Help Manage Risk
Low liquidity markets can act like wild animals. A single large order can throw price way off balance. That’s scary when you’re using stop losses or tight targets. High liquidity smooths out those bumps. Your technical analysis makes more sense when the market isn’t being whipsawed by random price gaps.
Real-World Examples of Liquidity Impact
Comparing EUR/USD vs USD/TRY
I placed trades on both EUR/USD and USD/TRY during the same market session. The difference was huge. On EUR/USD, the spread was under 1 pip and execution was instant. On USD/TRY, I waited over 2 seconds, and the spread was nearly 10 pips. That’s the cost of low liquidity.
With EUR/USD, you can place big orders without moving the market much. But in exotic pairs like USD/TRY, even a medium trade can trigger a noticeable price jump. That makes scaling or tight stop strategies almost impossible in thin markets.
Off-Hours Trading = Wider Spreads
Another time, I tried trading GBP/USD around midnight GMT. That was a mistake. Liquidity drops heavily during the overlap between the US close and Asia open. I noticed spreads widened from 1.2 pips to over 4 pips, and there was way more slippage.
So now I stick to the London and NY sessions. These are the busiest hours when most institutional players are active, making liquidity much higher. If you trade during off-hours, just know your execution will likely suffer.
News Events + Low Liquidity = Chaos
Economic news releases like the NFP (Non-Farm Payrolls) cause major price movements. But if they hit during a low liquidity moment, it’s chaos. One time, I had a short on USD/CAD right before a surprise interest rate hike. My stop loss slipped by 15 pips because liquidity vanished for a moment. It was brutal.
That’s why it’s smart to avoid placing orders right before news—especially if you’re in an exotic pair or trading outside the main sessions.
How to Trade Forex with Liquidity in Mind
Choose Pairs Based on Liquidity
Liquidity should influence the pairs you trade. Stick with majors like EUR/USD, USD/JPY, and GBP/USD if you want reliable execution and lower costs. Unless you have a specific edge in exotic pairs, I recommend staying clear. They’re just not worth the headaches most of the time.
Trade During the Right Time of Day
Forex market is a 24-hour market, but not all hours are equal. The best time to trade is during session overlaps:
- London/New York overlap (12–16 GMT) – Highest liquidity
- London open (7–9 GMT) – Strong movement and tight spreads
Early Asia session? That’s when I grab coffee, not trades. Spreads are too wide and price action is slow.
Use Tools That Show Market Depth
Some brokers give you access to depth-of-market tools (DOM). This shows how many orders are stacked at different price levels. If you don’t have this, look at real-time spreads and tick data. Fast price updates and small spreads mean better liquidity.
FAQs About Liquidity in Forex
What does high liquidity mean in forex?
High liquidity means there are lots of active buyers and sellers. This allows trades to be executed quickly and at stable prices with minimal slippage and tight spreads.
Which forex pairs are most liquid?
The most liquid pairs are the majors: EUR/USD, USD/JPY, GBP/USD, and USD/CHF. These are traded globally with the highest volume, offering the best execution conditions.
How does liquidity affect spreads?
In high liquidity markets, spreads are tighter because competition between buyers and sellers is strong. In low liquidity markets, spreads widen due to fewer participants and more risk for brokers.
Is low liquidity bad for trading?
Yes, usually. Low liquidity means higher spreads, more slippage, and unpredictable price movements. It makes risk management harder and trading more expensive.
Why is EUR/USD the most traded pair?
EUR/USD is the most liquid pair because it involves the two biggest economies—the U.S. and the Eurozone. This leads to huge trading volume and the tightest spreads.
Here’s What You Should Remember
We’ve covered a lot. Let’s quickly recap:
- Liquidity is key—it impacts your spreads, execution, and trading costs.
- High liquidity pairs like EUR/USD are cheaper and faster to trade.
- Low liquidity pairs come with higher costs and greater risk.
- Timing matters—trade during peak sessions to benefit from better liquidity.
If you want better results, you’ve got to pay attention to liquidity. It’s the difference between smooth sailing and trading in quicksand.
Now that you know how it works, use that knowledge to pick the right pairs, trade at the right time, and save yourself from nasty surprises. The more liquid your trade, the more control you’ll have. And in forex, control is everything.
