When I first stumbled into the world of Forex trading, I was overwhelmed. Charts everywhere. Flashy indicators. And a sea of unfamiliar words like “pip,” “lot,” or “spread.” Honestly, I felt like I was reading a different language. And maybe you’re feeling that too.
Here’s the thing: if you don’t know the basic terms, you can’t really understand what’s happening on your trading screen. That lack of clarity? It’s dangerous. It leads to emotional trades, confusion, and avoidable losses.
So I made it my mission to learn the core Forex vocabulary. And once I did? Everything started making sense.
This guide covers:
- Currency pairs, bid/ask, and spreads
- Trade mechanics like pips, lots, and margin
- Order types and how to protect your trades
- Concepts like slippage, liquidity, and carry trade
My goal: Help you speak the language of Forex like a pro — even if you’re just starting today.
What Is Forex Terminology?
Forex terminology is simply the vocabulary used in the foreign exchange market. It includes words and phrases traders use to describe currency prices, trading actions, risk settings, and strategy steps.
If you’ve ever stared at MetaTrader 4 or a Forex broker’s interface and felt lost, you’re not alone. I was there. The difference between success and struggle often lies in mastering these terms early.
Why These 25 Terms Matter
Trading without knowing these basics is like trying to fly a plane without understanding the controls. These 25 terms help you:
- Make sense of your trading platform
- Understand market moves
- Use risk management tools properly
- Read broker reviews and analysis without guessing
I’ve seen traders blow their accounts simply because they didn’t grasp what “leverage” or “margin call” really meant. Trust me — words matter here.
Essential Forex Terms You Must Know
Currency Pairs & Structure
All Forex trades involve currency pairs — two currencies traded against each other. For example, in EUR/USD, the EUR is the base currency and USD is the quote currency. It tells you how much USD you need to buy 1 EUR.
Base/Quote: This structure is essential to pricing. If EUR/USD = 1.1000, then 1 EUR = 1.10 USD.
When I finally understood that structure, I stopped confusing myself trying to figure out which currency I was buying or selling.
Trade Mechanics & Orders
Let’s talk pips. A pip is the smallest move a currency pair can make. For most, it’s the fourth decimal place. For yen pairs, it’s the second. Example: If EUR/USD moves from 1.1000 to 1.1005, that’s a move of 5 pips.
Then there’s the lot size. A standard lot is 100,000 units. You can also trade mini lots (10,000) or micro lots (1,000). Choosing the wrong lot size nearly blew up my account once — so double-check yours.
And the bid/ask spread? That’s the difference between the buying and selling price — it’s how brokers get paid. The tighter the spread, the better for you.

Leverage, Margin & Risk
This is where things get risky fast. Leverage lets you control a large trade with a small amount of money. If your leverage is 100:1, a $100 deposit lets you control $10,000 in trades.
But that power cuts both ways. That’s why brokers require a margin — a deposit that ensures you can cover losses. When your margin drops too low, you get a margin call — and that means your trade might be closed automatically.
I once ignored margin levels while chasing a trade. Bad idea. Don’t be like me — understand your broker’s requirements.
Trade Strategies & Positions
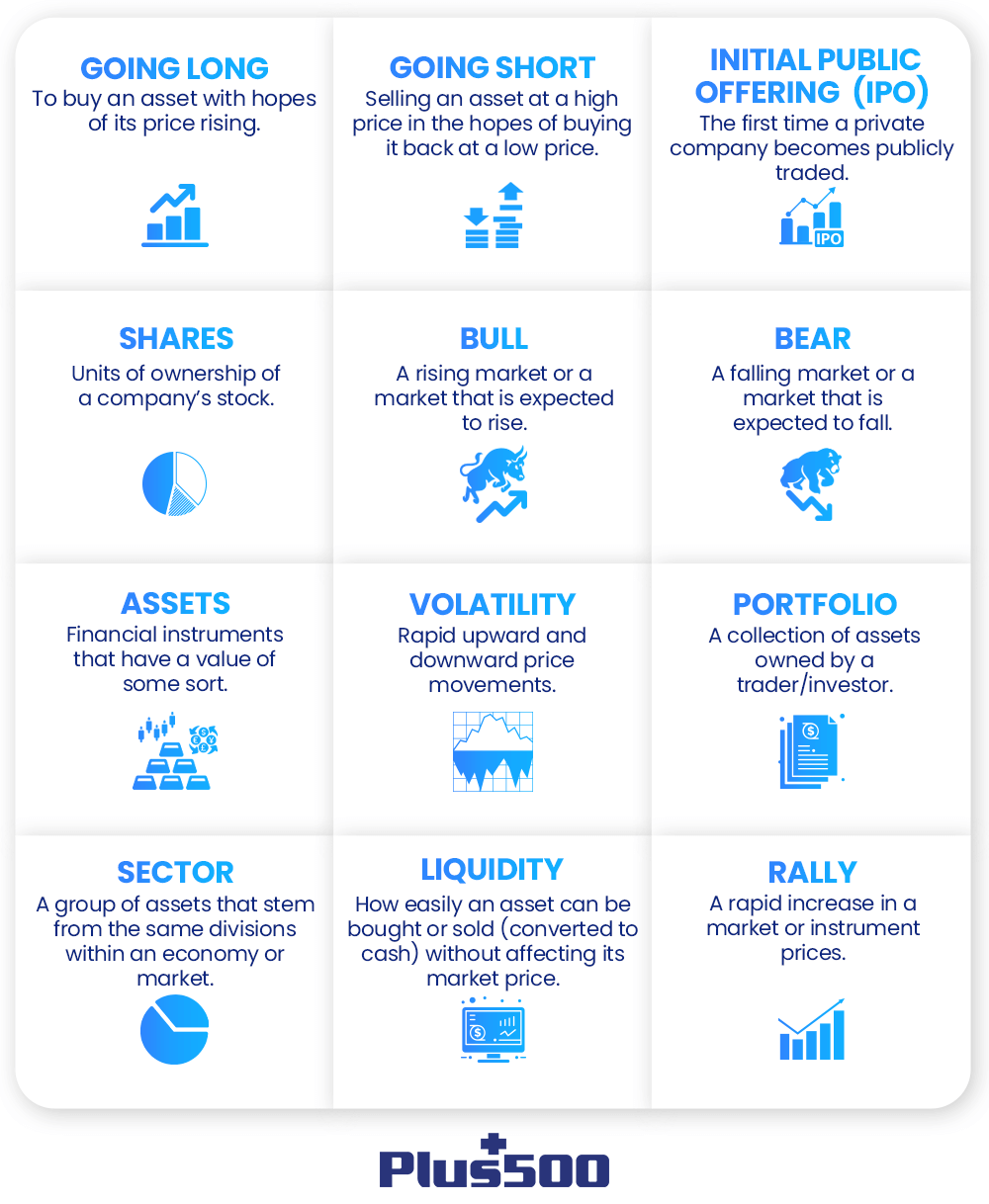
If you expect prices to rise, you go long. That’s called a bullish position. If you expect a drop, you go short — also known as being bearish.
You’ll often hear traders talk about support and resistance. These are price levels where markets tend to bounce off or stall. Learning these changed how I used stop-losses — it made my entries and exits so much smarter.
Order Types & Execution
Placing the right kind of order matters more than you think. A market order executes instantly at the current price. A limit order only executes at your specified price — or better.
A stop-loss order automatically closes a losing trade at a set price, preventing bigger losses. A take-profit order does the opposite — locking in gains when your target is hit. These tools saved me more times than I can count.
Trading Environment Concepts
Volatility tells you how fast prices are moving. Fast swings? High volatility. Slow, steady moves? Low volatility. More volatility usually means more risk — and more opportunity.
Liquidity refers to how easily a currency pair can be bought or sold. Major pairs like EUR/USD are highly liquid — meaning tighter spreads and faster execution.
Slippage happens when your order executes at a worse price than expected — usually during fast market moves or low liquidity. It’s annoying, but it’s part of the game.

Broader Concepts & Tools
Carry trade is a strategy where you borrow in a low-interest currency and invest in a higher-interest one. You earn the difference (called the “carry”). Sounds cool, right? But it only works in stable market conditions.
Risk management is the real secret of long-term success. Using stop-losses, managing leverage, and trading with discipline? That’s how pros survive — and thrive.

Real-World Example: Applying These Terms in a Trade
| Term | How It Applies |
|---|---|
| Currency Pair | Trader chooses EUR/USD to trade |
| Leverage | Uses 50:1 leverage to open a $5,000 position with $100 |
| Spread | Broker offers a 1.2 pip spread |
| Stop-Loss | Set at 20 pips below entry to manage risk |
| Take-Profit | Set at 40 pips above entry to lock profits |
In that simple trade setup, I used at least five of the core terms from this list. Doing it right made all the difference.
Common Mistakes Beginners Make With Forex Terminology
Confusing Leverage With Profit Potential
Early on, I thought more leverage meant more profit. And technically, that’s true. But it also means more risk. I learned the hard way when a small pip move wiped out my entire account. Leverage magnifies everything — good or bad. If you don’t fully understand how it works, stay on the low side.
Misunderstanding Margin Requirements
One of my first trades got stopped out not by price, but by a margin call. Why? I didn’t realize my broker needed a minimum margin level to keep the trade open. Always know your margin usage and how much wiggle room you have before that call hits.
Improper Use of Stop-Losses
New traders often skip stop-losses or place them too tight. I used to put mine 5 pips away — they’d get hit instantly. Now I place them just below key support levels. The key? Know where the market is likely to turn and place your safety net accordingly.
How to Keep Learning Forex Terminology
Use Interactive Tools and Apps
I started using cheat sheets, mobile apps, and browser extensions that define Forex terms in real-time. They helped me absorb the language just by trading. You’ll find plenty of these in platforms like BabyPips or the Vantage Markets education hub.
Download and Review Glossaries
Print a PDF glossary and stick it near your trading desk. I had one from Plus500 that helped me memorize every key term. Having something physical to refer to is surprisingly helpful when you’re starting out.
Quiz Yourself Often
Don’t just read the terms — test your understanding. I created flashcards and took online quizzes regularly. It’s a great way to reinforce what you learn. And if you’re in a trading community, quiz each other to make it fun.
FAQs
What are the most important Forex terms for beginners?
If you’re just starting out, focus on understanding pips, lots, leverage, margin, bid/ask, spread, stop-loss, and take-profit. These form the foundation of every trade. Without them, you’re just guessing.
How do I calculate pip value in Forex?
For most currency pairs, one pip equals 0.0001. The value depends on your lot size and currency. For example, 1 pip on a standard lot (100,000 units) is usually worth $10. Many platforms calculate it for you automatically, but it’s good to know the math.
What’s the difference between spread and slippage?
Spread is the cost you pay to enter a trade, the difference between bid and ask price. Slippage happens when your order executes at a different price than expected, usually in fast-moving markets.
Why do bid and ask prices matter in trading?
The bid is the price you sell at, and the ask is the price you buy at. The difference is the spread — your transaction cost. Tighter spreads usually mean better trading conditions.
What is leverage and how does it work?
Leverage lets you control a larger trade with a small deposit. If you have 50:1 leverage, $100 lets you control $5,000 in trades. But remember, bigger trades mean bigger risks. Use leverage wisely or it will burn you.
Recap of Key Points
We covered a ton — from how currency pairs work to placing the right stop-loss. I walked you through pips, lots, leverage, and even threw in real-world scenarios to show how these terms play out in actual trades.
Final Takeaway
If you want to grow as a trader, start by speaking the language. These 25 terms aren’t optional — they’re your toolkit. Whether you’re demo trading or live, knowing these will save you from costly mistakes.
Closing Thought
I’ve been in your shoes — confused, frustrated, and ready to give up. But once I understood the language of Forex, everything changed. I traded smarter, lost less, and started winning more. You can too. Learn these terms. Bookmark this page. And come back anytime you need a refresher. I’ve got your back.
